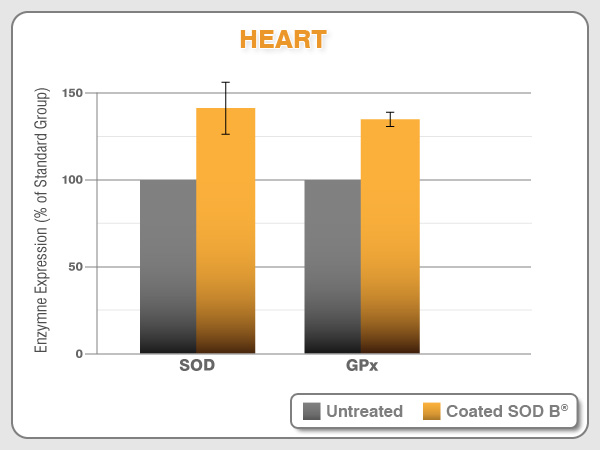
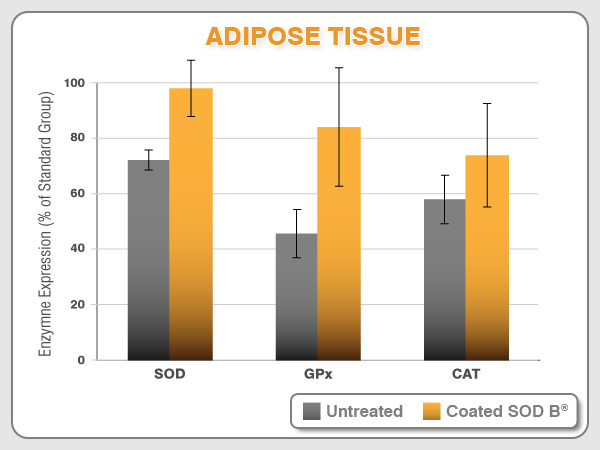
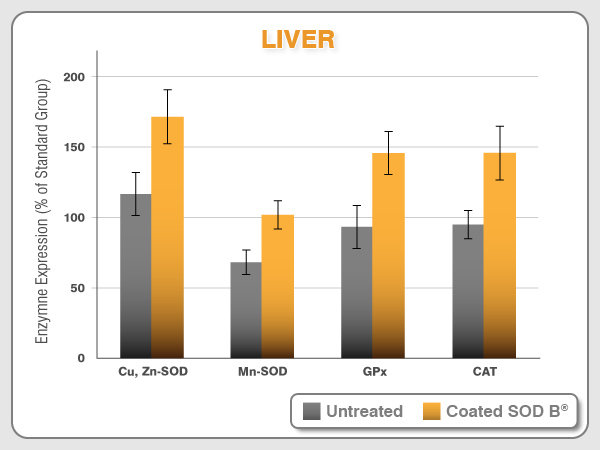
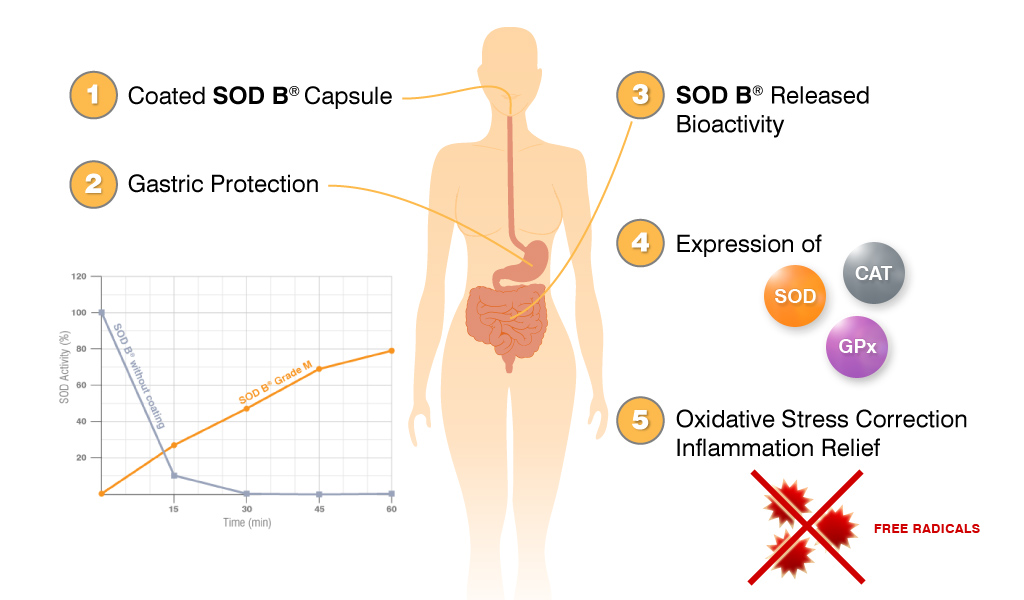
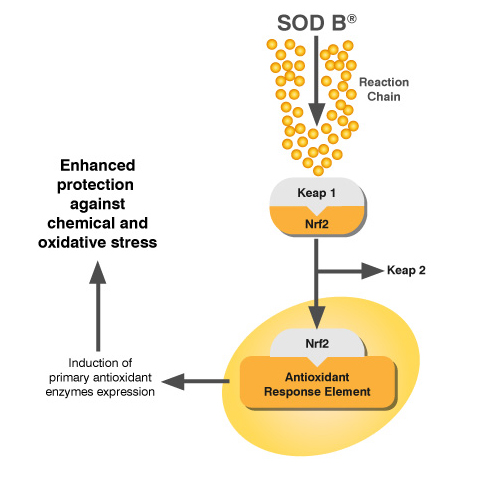
SOD B® stimulates primary antioxidant levels
SOD B® is released along the intestinal tract thanks to the gastric-protection provided by the coating. However, coatings only protect SOD from the digestive process and can’t help SOD to cross the intestinal barrier. As a protein, SOD has a high molecular weight and can’t be bioavailable and reach the blood circulation. After 10 years of research, the Bionov research team have shown on several animal models and in different targeted tissues that an oral SOD B® supplementation induces the expression of the own body’s endogenous primary antioxidant defenses: SOD, CAT, and GPx.
 English
English Français
Français