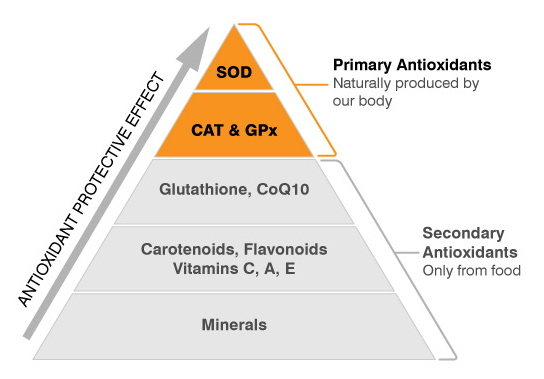
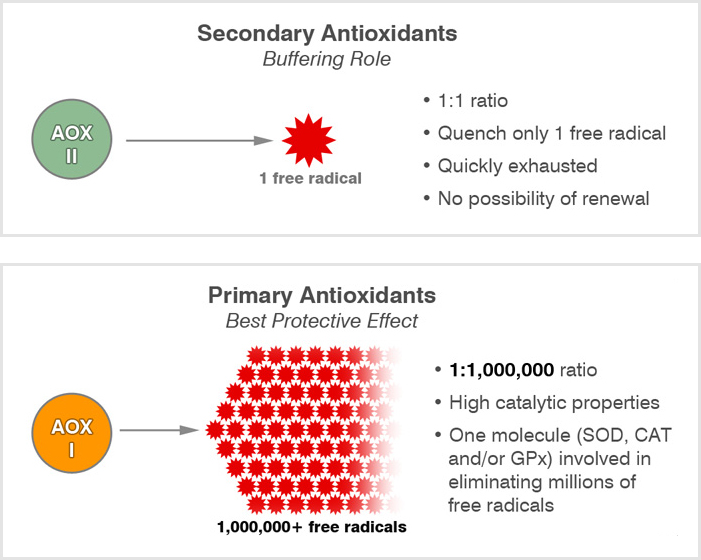
Primary-antioxidants are essential antioxidant enzymes naturally produced by our body. These internal antioxidant enzymes serve as our body’s most potent defense against free radicals and harmful inflammatory reactions. There are only 3 primary-antioxidants: SOD, Catalase (CAT) and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx). Thanks to their complementary and synergic mechanism of action against free radicals, SOD, CAT and GPx prevent the development of oxidative stress. Secondary antioxidants are externally provided from dietary sources, such as vitamins (Vitamins C and E), minerals (Se, Cu, Zn, Mn) carotenoids and flavonoids.
“The most valuable antioxidants aren’t the ones you eat but the ones our own body produces.”
 English
English Français
Français